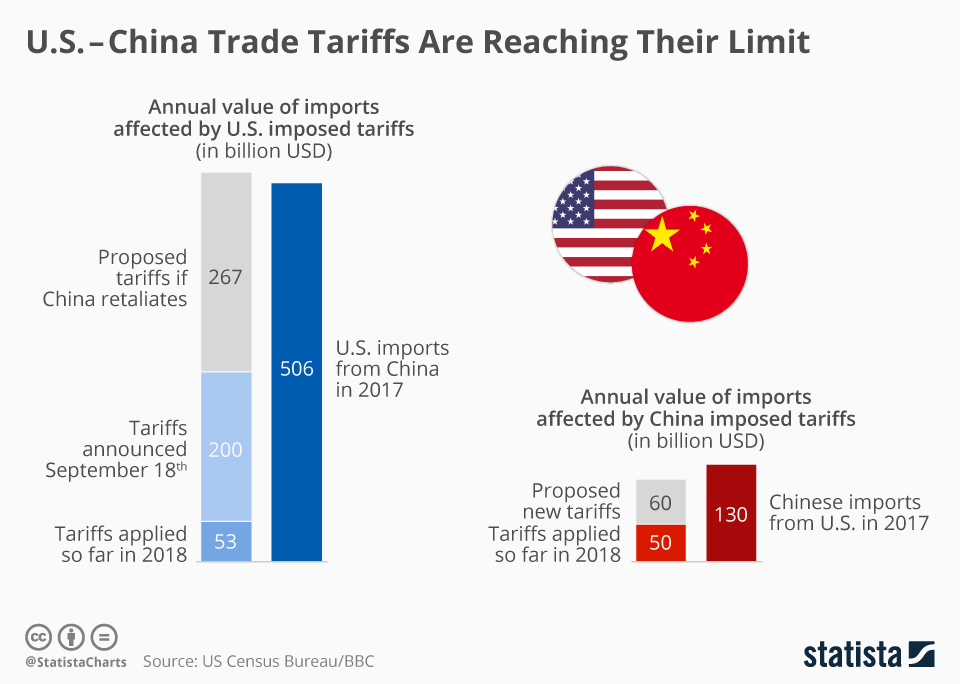
The impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy has sparked significant debate among economists and policymakers. As tensions rise in the U.S. trade war, the imposition of hefty tariffs threatens to escalate costs for American consumers while simultaneously straining foreign relations with China. Analysts caution that these tariffs could lead to increased prices on everyday goods and supply chain disruptions across various sectors. Moreover, if tariffs reach proposed levels, their effect could ripple through labor markets, potentially causing shortages and a squeeze on household budgets. With these consequences looming, understanding the broader implications of U.S.-China trade dynamics has never been more critical for the American economy.
The repercussions of imposing tariffs on Chinese imports resonate deeply within the U.S. economy, inciting widespread concern regarding trade relations. This ongoing trade conflict, often referred to as the U.S.-China trade war, holds the potential to reshape economic interactions between the two nations. As tariffs are enacted, they not only impact prices for consumers but also threaten critical supply chain stability, raising alarms in industries reliant on Chinese goods. Furthermore, this trade tension could push China to strengthen ties with other major economies, altering global economic landscapes. It is crucial to examine how such fiscal policies could influence both local economic conditions and broader international relations.
Understanding the Economic Landscape: Tariffs and the U.S. Economy
The imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports is a decision that transcends mere economic policy; it strikes at the very core of international relations and impacts the U.S. economy significantly. As tariffs on Chinese goods increase, Americans can expect a rise in prices for everyday products. This inflation happens as companies face higher costs associated with sourcing materials and manufacturing. Economists warn that these tariffs can lead to supply chain disruptions, affecting not just luxury items but also essential goods, which will burden consumers with higher prices across the board.
In addition to immediate price concerns, the larger implications of China tariffs on the U.S. economy may create ripple effects in terms of job security and market stability. Companies that rely heavily on imported Chinese goods may face operational challenges that require layoffs or reduced hours for workers. Labor shortages, particularly in sectors dependent on timely imports, could exacerbate existing economic issues in the U.S., leading to increased public dissatisfaction and further complications in U.S.-China relations.
Unintended Consequences: Tariffs and Foreign Relations
The potential for tariffs to adversely affect U.S. foreign relations cannot be overstated. While the intention behind imposing tariffs is often to protect American jobs and industries, it can inadvertently strain relationships with key allies. Countries such as the U.K., Australia, and Japan, which have historically shared trade ties with the U.S., may feel compelled to reassess their economic partnerships if they perceive a threat from U.S. trade policies. This diplomatic fallout may allow China to strengthen its own ties with these nations, creating a shift in global alliances.
Moreover, if the U.S. adopts a broad approach to tariffs that targets multiple countries, this could unify Beijing and U.S. allies against a common challenge. Economists and political analysts suggest that this coalition-building might not just benefit China economically but also mitigate diplomatic isolation. By fostering solidarity among affected nations, China may forge new trade partnerships, leading to long-term shifts in global trade dynamics that may be detrimental to U.S. interests.
The Supply Chain Disruption Dilemma
Supply chain disruptions emerge as a significant consequence of increased tariffs on Chinese goods, affecting a wide range of industries. The intricate web of global trade means that many products now rely on various components sourced from different countries, including China. Tariffs create uncertainty that disrupts this delicate balance. Companies may struggle to find alternative suppliers quickly, jeopardizing production schedules and leading to losses. As businesses scramble to adapt, they may face higher operational costs, which are often passed on to the consumer.
In navigating these disruptions, many U.S. companies could explore diversifying their supply chains by outsourcing production to countries like Vietnam or India. While this could mitigate some risks associated with dependency on China, the transition period is fraught with challenges, such as establishing quality standards and navigating local regulations. The potential for increased prices and product delays looms large, perpetuating the economic strain on the consumer and the U.S. economy at large.
China’s Economic Strategy and Response
China stands at a crossroads, faced with the possibility of renewed tariffs on its exports to the U.S. This looming threat has prompted a reevaluation of its economic strategies, particularly as Beijing grapples with a sluggish housing market and diminishing consumer demand. Economists suggest that China may seek to enhance its trade relationships with other economies, such as those in the European Union and Southeast Asia, to cushion the blow from U.S. tariffs. This shift could enable China to pivot, minimizing reliance on the American market.
Moreover, China’s ambitious Belt and Road Initiative shows its commitment to expanding its economic footprint globally, seeking new markets to offset potential losses from tariffs. This initiative not only aids in diversifying China’s trade partners but also strengthens economic ties with developing nations, solidifying its position as a major player in global trade. By doing so, China may reduce its vulnerability to U.S. trade policies while simultaneously enhancing its influence abroad.
The Future of U.S.-China Trade Relations
As the U.S. approaches the potential for heightened tariffs, the future of its trade relationship with China hangs in the balance. Recent discussions surrounding tariff rates indicate that aggressive policies may exacerbate existing tensions between the two countries. The uncertainty created by fluctuating tariff rates can hinder both nations’ economic growth, impacting not only their domestic markets but also the global economy. If implemented, high tariffs could instigate a retaliatory cycle, where both countries engage in an escalating trade war that ultimately serves no one well.
However, there exists an opportunity for dialogue and negotiation, ideally leading to a compromise that may mitigate the harsh impacts of tariffs. By focusing on cooperation rather than confrontation, the U.S. and China could explore mutually beneficial trade agreements that address underlying issues while fostering economic stability. This would not only benefit both economies but could also serve to improve diplomatic relations and restore faith in international trade systems.
China Tariffs Impact on the U.S. Economy: A Double-Edged Sword
The decision to impose new tariffs on Chinese imports presents a double-edged sword for the U.S. economy. While aimed at protecting domestic industries, such measures can backfire, leading to inflationary pressures on American consumers. The cost of everyday items, from electronics to essential goods, could escalate significantly as companies grapple with increased import expenses. Many analysts warn that this inflation could stifle consumer spending, ultimately leading to a slowdown in economic growth.
Additionally, by raising tariffs, the U.S. risks igniting a retaliatory response from China, forcing American companies to rethink their supply chain strategies and potentially moving production overseas. This could result in job losses domestically as businesses react to decreased competitiveness in the global market. The long-term effects of these tariffs could destabilize the U.S. economy, ultimately pushing Americans to pay more for less, while compromising the economic relationships that have been built over decades.
The Trade War’s Toll on Consumer Prices
One immediate impact of tariffs on Chinese goods is the upward pressure they place on consumer prices. As American businesses seek to maintain their profit margins amidst rising costs, they may choose to pass these increases directly onto consumers. This leads to higher prices in retail environments, making basic goods less accessible to the average American. Areas such as electronics, clothing, and household items are particularly vulnerable to these inflationary trends, which can significantly alter consumer behavior.
Furthermore, the ramifications of a spike in consumer prices extend beyond the retail sector. Economists suggest that as consumers limit their spending in response to increased prices, broader economic growth can stall. This cautious spending behavior can adversely affect businesses reliant on a healthy flow of consumer income, ultimately putting jobs at risk. The continued trade war and its consequences serve as a reminder of the complexities involved in tariffs and their impact on everyday Americans.
New Market Opportunities Amidst Trade Tensions
In the face of increasing tariffs, there may be unexpected opportunities for U.S. businesses to explore new markets outside of China. Companies may pivot towards suppliers in countries such as India and Vietnam, where manufacturing costs could be lower. This shift could also encourage innovation and diversification within supply chains, allowing businesses to reduce reliance on a single market. Such a strategy may yield competitive advantages in the long term, encouraging companies to build resilience against future trade disruptions.
However, exploring new markets is not without its challenges. Businesses must carefully evaluate the capabilities of potential suppliers and the feasibility of relocating production lines. It requires investment in building relationships, adapting to different business practices, and ensuring quality standards. The transition period can pose significant hurdles; nonetheless, for U.S. businesses, this shift could herald a new era of trade dynamics as they navigate the complexities of the global market.
Geopolitical Implications of a Trade War
The geopolitical landscape of U.S.-China relations stands to shift dramatically should the U.S. follow through with significant tariff increases. With heightened tensions, China could find common ground with other nations impacted by U.S. trade policies, realigning global trade alliances. This coalition-building might weaken traditional ties between the U.S. and its allies, potentially altering the balance of power within international politics.
In addition, a more insular approach to trade by the U.S. may embolden China to assert its influence in regions traditionally dominated by American economics. Through initiatives like the Belt and Road, China could strengthen relationships with key markets in Southeast Asia and Africa, facilitating its dominance in global trade networks. The long-term implications of these shifts reveal the intricate connections between trade policies and international diplomacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy?
China tariffs have a complex impact on the U.S. economy, leading to increased costs for consumers and businesses due to higher prices on imported goods. This can result in inflation and potential disruptions in supply chains, affecting everything from electronics to everyday products. Economists warn that prolonged tariffs could hinder economic growth and strain U.S.-China relations.
How do tariffs affect supply chain disruptions related to China?
Tariffs imposed on Chinese goods can cause significant supply chain disruptions as manufacturers may struggle to source materials at cheaper costs. This can lead to delays in production times, increased operational costs, and a need for businesses to seek alternative suppliers, which is often a time-consuming process.
What role do China tariffs play in the U.S. trade war?
China tariffs are a central aspect of the ongoing U.S. trade war, which aims to address trade imbalances and force China to adhere to fair practices. However, these tariffs can lead to retaliatory measures from China, exacerbating tensions and complicating foreign relations with other nations involved in trade.
Could China tariffs lead to higher prices for American consumers?
Yes, the implementation of China tariffs is likely to lead to higher prices for American consumers as import duties increase the cost of goods from China. This could particularly impact sectors reliant on Chinese manufacturing, such as technology and consumer goods, ultimately affecting consumer spending and overall economic health.
What are the potential long-term effects of tariffs on U.S.-China foreign relations?
The long-term effects of tariffs on U.S.-China foreign relations could be detrimental, potentially fostering a divide that encourages China to strengthen ties with other nations. This shift could weaken traditional alliances of the U.S. and provide China with newfound leverage on the global stage.
How might tariffs impact the China economy and American exports?
Tariffs could severely impact the China economy by reducing its exports to the U.S., which represent a significant portion of its total trade. This drop in demand may force China to pivot its focus to emerging markets but could ultimately lead to slower economic growth and possible instability.
What opportunities might arise for other countries due to reduced Chinese imports in the U.S.?
If Chinese imports decline due to tariffs, countries such as India and Vietnam may see opportunities to fill the supply gap. However, this transition may take time as these nations would need to enhance their manufacturing capabilities and supply chain infrastructures to meet U.S. demand effectively.
Could the U.S. tariffs on China lead to a currency war?
Yes, U.S. tariffs on China may trigger a currency war, where both countries devalue their currencies to maintain competitiveness. This could further complicate trade relations and create economic instability in both economies as they strive to protect their export markets.
How are U.S. consumers likely to react to the effects of China tariffs?
U.S. consumers may react negatively to the effects of China tariffs as they experience rising prices and a potential reduction in product availability. This could impact consumer behavior and overall economic sentiment, leading to decreased spending in other sectors.
Is the U.S. prepared for the possible economic fallout from escalating tariffs on China?
While the U.S. government may have strategies to mitigate the economic fallout from escalating tariffs on China, the extent to which these plans will be effective remains uncertain. Economists emphasize the need for careful planning to avoid significant disruptions within the economy and trade relationships.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Impact of Tariffs on Prices | Imposing tariffs could lead to increased prices for American consumers due to higher costs of imported goods. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Heightened tariffs might disrupt existing supply chains, leading to labor shortages and potential inflation. |
| U.S.-China Relations | Increased tariffs could strain diplomatic relations, pushing China closer to U.S. allies, potentially weakening traditional partnerships. |
| Opportunities for China | Tariffs might provide China with opportunities to engage European allies against U.S. trade policies. |
| China’s Economic Challenges | China’s economy is already facing challenges such as sluggish demand and a faltering housing market. |
Summary
The China tariffs impact on the U.S. economy is profound, presenting a complex web of consequences for both nations. While aimed at weakening China’s economy, the penalties may inadvertently escalate prices for American consumers and disrupt vital supply chains, leading to broader economic instability. Additionally, such aggressive trade policies risk undermining U.S. relations with allies as China seeks to forge stronger connections with nations like the EU and Japan, potentially altering global economic dynamics. Hence, understanding the China tariffs impact on the U.S. economy is crucial for forecasting future trade relations and economic resilience.