The housing affordability crisis is reshaping the American dream, pushing homeownership farther out of reach for many families. In the bustling housing market, soaring prices and diminishing availability of homes have sparked urgent discussions about effective solutions. Factors such as land-use regulations and the pervasive effects of NIMBYism have stifled construction productivity and innovation, ultimately contributing to this growing crisis. As builders grapple with increasing compliance demands and community objections, the ability to deliver affordable homes diminishes. Now, more than ever, it’s crucial to analyze how these housing market trends impact our economy and explore innovative approaches to resolve a predicament that threatens to destabilize social equity and economic mobility.
The ongoing struggle for affordable housing reflects not just a singular issue but a broader challenge encompassing various elements of the real estate landscape. As rising costs and limited housing supply create hurdles, alternative terms like the “housing affordability dilemma” highlight the urgency of this situation. The complexities of local land-use policies and their implications on new construction reveal how community resistance, often labeled as NIMBYism, exacerbates the crisis. By understanding the interrelated factors affecting construction efficiency and real estate innovation, we can formulate strategies that foster greater accessibility for prospective homeowners. Addressing this multifaceted challenge is essential for ensuring a balanced and thriving housing ecosystem.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
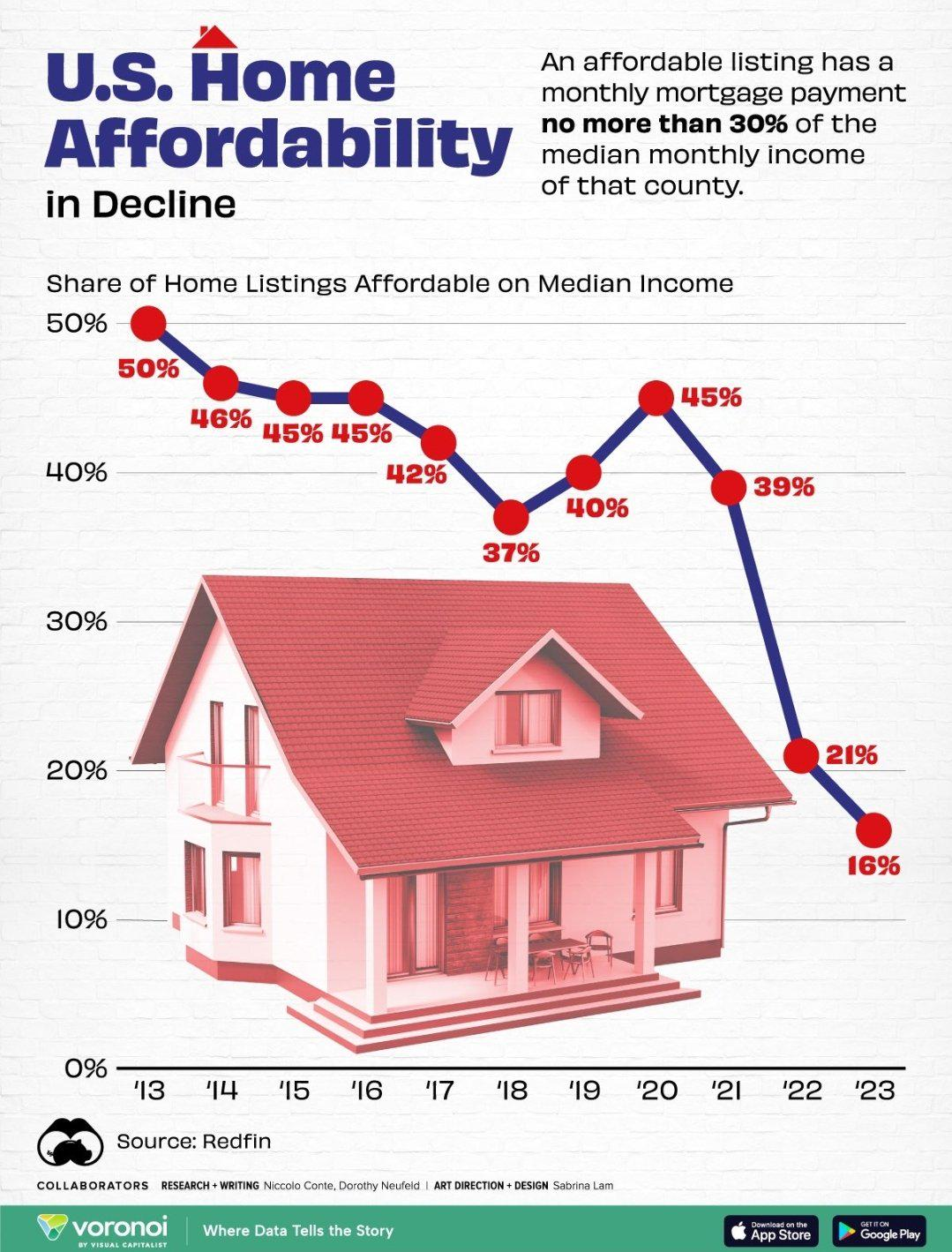
The housing affordability crisis in the United States is a growing concern that affects a significant portion of the population. As home prices continue to soar, many Americans find themselves unable to afford a place to live. Factors contributing to this crisis include rising labor and material costs, but perhaps even more critical are the restrictive land-use regulations that have emerged in various communities. These regulations, often driven by NIMBYism, have stifled the development of new housing projects, leading to a sharp decline in the availability of affordable housing options.
Moreover, the housing market trends illustrate a clear divergence between the construction productivity of past decades and the current state of the industry. Traditionally, large-scale developers were able to construct vast housing projects efficiently, which greatly reduced overall home costs. However, modern building practices, hindered by stringent zoning laws and small-scale developments, have resulted in a stagnation of innovation in the real estate sector. This decline in productivity not only exacerbates the housing affordability crisis but poses significant challenges for future generations seeking homeownership.
The Impact of NIMBYism on Housing Development
NIMBYism, or ‘Not In My Backyard’ attitudes, significantly influences land-use regulations and housing development in communities across the nation. While community members may advocate for preserving their local environment and maintaining property values, these intentions can lead to restrictive policies that hinder new constructions. Such regulations can limit the size and scope of housing projects, thereby reducing the number of affordable homes available on the market. This pushback against larger developments often leads to bureaucracy that stifles the ability of builders to innovate and produce housing efficiently.
As more areas adopt NIMBY policies, we witness a disparity in the housing supply versus demand dynamic. This stunted growth in housing availability correlates with rising real estate prices and limited options for aspiring homeowners. Instead of fostering an environment where developers can experiment with new ideas and cost-effective building methods, these restrictive practices lead to a homogeneous and outdated housing market. Addressing the implications of NIMBYism is crucial for reversing the trends that have contributed to the current housing crisis.
Revisiting Land-Use Regulations for Better Productivity
Land-use regulations, while often created with good intentions, have proven to be a double-edged sword in the housing market. Tighter controls inhibit not only the production of new homes but also the capacity for builders to achieve economies of scale. This lack of large-scale housing projects means less efficient production methods are employed, ultimately leading to higher costs for consumers. The relationship between decreased housing productivity and stringent regulations reveals a pressing need for reevaluation to align community interests with necessary housing developments.
Proposals for reforming land-use regulations could include simplifying approval processes and encouraging larger developments that meet community needs. By fostering an environment that supports innovative construction practices, it becomes possible to achieve a balance between local engagement and the urgent need for affordable housing solutions. Fostering constructive dialogue among stakeholders may pave the way for legislative changes that not only prioritize community welfare but also address the crippling affordability crisis affecting millions.
The Role of Construction Innovation in Housing Affordability
Construction innovation plays a pivotal role in driving down costs and increasing housing availability. Historically, advancements in building technologies and methods have allowed for the development of more efficient, cost-effective homes. However, recent patterns suggest a stagnation in innovation within the construction sector, largely resulting from restrictive land-use policies and traditional building practices. This stagnation has hindered the ability of builders to respond dynamically to the housing demand, thus exacerbating the affordability issues many face today.
Exploring pathways for innovation in construction can bring about transformative changes in the housing market. Embracing new technologies such as modular construction, sustainable building materials, and smart home integrations can significantly enhance productivity. Furthermore, by fostering an innovation-friendly regulatory environment, stakeholders can facilitate a revival of the construction boom reminiscent of the mid-20th century. Such shifts are essential for constructing affordable housing and revitalizing the overall housing market for future generations.
Economic Consequences of the Housing Crisis
The economic consequences of the housing affordability crisis extend far beyond individuals struggling to purchase homes. When large swathes of the population cannot afford housing, it triggers a ripple effect throughout the economy. Businesses may struggle to find employees who can afford to live within commuting distance, leading to a labor shortage that stunts economic growth. Additionally, when young families cannot invest in homes, the overall market suffers from reduced consumer spending and investment, which can lead to stagnation in both local and national economies.
Moreover, the transfer of wealth often favors older generations who already own home equity, further entrenched by the lack of accessible housing for younger demographics. This transfer creates a financial disparity that could have long-term implications on economic mobility and stability. Addressing the core issues leading to the housing crisis is imperative for fostering a sustainable economy where all citizens have the opportunity to thrive, thereby strengthening our communities and the nation as a whole.
The Future of Housing: Balancing Needs with Regulations
Looking ahead, the challenge will be to balance the growing needs for affordable housing with the existing land-use regulations that currently hinder development. As urban areas continue to grow, the demand for housing will only increase, prompting the need for innovative solutions that address NIMBYism and complex regulations. Initiatives that foster community involvement in housing development decisions—while simultaneously promoting larger scale projects—can help address these pressing concerns.
In addition, strategic collaborations between government entities, urban planners, and community stakeholders can pave the way for effective policies that emphasize smart growth and responsible land use. Exploring innovative approaches, like public-private partnerships in developing affordable housing, could serve to create a beneficial framework that satisfies community desires while also meeting housing demands. The future of housing hinges on our ability to adapt and reform outdated practices to ensure sustainable growth.
The Importance of Large-Scale Housing Projects
The current housing crisis highlights the importance of large-scale housing projects in responding to the burgeoning demand for affordable homes. Historically, developments that could build thousands of homes at once have played a crucial role in keeping housing prices manageable. As the ratio of large-scale constructs to smaller projects declines, overall productivity suffers, leading to higher prices for consumers. Reviving large-scale housing initiatives is essential to provide the volume of housing needed to alleviate the affordability crisis.
Encouraging the development of large housing projects requires overcoming local resistance often rooted in NIMBY attitudes. Strategies that include community outreach, transparent communication, and demonstrating the value of these projects can help galvanize support. Demonstrating how large developments can sustainably integrate into existing communities—preserving their unique character while offering much-needed housing—will be key to reshaping how we tackle the challenges posed by the current housing market.
Strategies to Increase Construction Productivity
To address the decline in construction productivity, stakeholders must implement strategies that encourage greater efficiency and innovation. Supporting training programs that focus on modern construction technologies and methods will empower builders to adopt practices that enhance productivity. By investing in research and development tailored to the construction sector, the industry can reinvent itself, fostering an environment where homebuilders can embrace new methods that drive down costs.
Additionally, simplifying zoning regulations and easing the bureaucratic barriers that often accompany large-scale projects can encourage builders to invest in innovative construction methods. Emphasizing collaborative approaches among builders, urban planners, and local governments to create streamlined processes will mitigate the delays often associated with project approvals. Such strategies are intended to stimulate productivity while ensuring that the housing market can effectively meet the growing demands of the American public.
Real Estate Innovations Reshaping the Housing Market
Innovation in real estate is essential not only for addressing the housing crisis but also for transforming the way we approach homebuilding and community development. From digital tools that facilitate real-time market analysis to advancements in eco-friendly building materials, these innovations can lead to smarter, faster, and more economical constructions. As builders adopt these technologies, they will enhance efficiency and increase the capacity to deliver homes that are both affordable and sustainable.
Adopting a mindset geared towards innovation requires openness to new methodologies and a willingness to embrace change. Harnessing the power of analytical tools to better understand housing trends and consumer needs can help developers make informed decisions that align with market demands. As we look to the future, fostering a culture of innovation within the real estate industry will be key to overcoming the challenges created by stagnant productivity and high housing costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between the housing affordability crisis and land-use regulations?
Land-use regulations have a significant impact on the housing affordability crisis. These regulations often limit the size and scope of construction projects, creating smaller developments that deter mass production of homes. This ultimately leads to higher costs because builders cannot achieve the economies of scale necessary for affordable housing.
How does NIMBYism contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBYism (Not In My Backyard) greatly contributes to the housing affordability crisis by hindering new construction projects. Local opposition to development leads to stricter zoning laws and land-use regulations, which reduces the number of homes built, driving prices up and making housing less accessible for many Americans.
What impact do housing market trends have on the housing affordability crisis?
Current housing market trends, characterized by low inventory and high demand, exacerbate the housing affordability crisis. As prices for homes rise due to limited supply, many individuals and families find ownership increasingly out of reach, highlighting the urgent need for innovative solutions in construction and real estate.
In what ways does construction productivity affect the housing affordability crisis?
Declining construction productivity has a direct impact on the housing affordability crisis. Lower productivity means fewer homes are being built efficiently and at a lower cost. As regulations increase and project sizes decrease, builders become less innovative and productive, leading to inflated housing prices.
How is real estate innovation related to the housing affordability crisis?
Real estate innovation is crucial to addressing the housing affordability crisis. New building methods and technologies can increase efficiency and reduce costs. However, the lack of innovation in the construction sector, partly due to stringent land-use regulations, hampers efforts to produce affordable housing solutions for consumers.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The price of new single-family homes has more than doubled since 1960, leading to ownership becoming out of reach for many Americans. |
| Impact of NIMBY Policies | Land-use regulations, influenced by NIMBYism, restrict builders from undertaking large-scale projects, negatively affecting productivity and innovation in the housing sector. |
| Productivity Decline | Construction productivity fell significantly from 1970, even as the overall economy grew, leading to fewer innovations and increased costs of new homes. |
| Comparison to Other Industries | While sectors like auto manufacturing saw productivity increases, the construction sector has struggled to innovate and adapt since the 1970s. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations have seen a drastic drop in housing wealth compared to older generations, indicating a growing economic divide. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis continues to be a pressing issue in the United States, exacerbated by restrictive land-use regulations and NIMBY (Not In My Back Yard) sentiments that stifle large-scale construction projects. As housing prices soar and homeowners become scarce, we must address these significant barriers that have contributed to a decline in construction productivity and innovation. With rising costs and limited access to homeownership, the crisis not only impacts the economy but also deepens the divide between generations. Immediate reform is necessary to build more homes, enhance affordability, and ultimately bring solutions to the housing affordability crisis.