The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly significant as technology reshapes the workforce landscape. Recent studies highlight how artificial intelligence is not only changing job roles but also forecasting a future of work where occupational churn could redefine employment patterns. While fears of AI job disruption have sparked debates about mass job loss, evidence suggests a complex interplay of growth in STEM job sectors and shifts in traditional roles. The current trends show an increase in skilled positions, which counters earlier assertions of job stagnation. As we delve deeper into this technological transition, understanding the dual nature of AI’s influence on employment—both empowering and potentially displacing jobs—becomes paramount.
Exploring the ramifications of machine learning advancements on employment dynamics reveals a multifaceted narrative of technological evolution. As innovations foster rapid changes in job roles, the conversation around workforce adaptation focuses on the future of work and its challenges. Many experts note an impending occupational transformation, characterized by significant shifts in required skill sets and job availability. The escalation of STEM roles signals a healthy adaptation to new technologies, even amid concerns about automation’s job displacement effects. Therefore, as the labor market evolves, it is crucial to navigate the balance between embracing technological benefits and addressing the jobs’ precarious nature in various industries.
The Evolution of Technology in the Labor Market
Over the past century, technology has woven an intricate tapestry within the U.S. labor market. Historically, the labor landscape has experienced continuous adaptation through advancements, from the agricultural revolution to the rise of manufacturing and now towards a predominance of technology-driven jobs. One key aspect of this transformative journey is the concept of “occupational churn,” which highlights how job roles evolve and emerge alongside technological advancements. As industries grow and adapt, workers often find themselves navigating a constantly shifting terrain, where new skills must be acquired to meet the demands of changing job requirements.
The research conducted by David Deming and his colleagues breaks down a century of labor dynamics, shedding light on the interplay between technological developments and employment trends. While the era from 1990 to 2017 seemed characterized by stability, reflective of a plateau in job role disruption, the recent emphasis on artificial intelligence has emerged as a game-changer, introducing new complexities. Understanding these historical trends not only helps in grasping past labor shifts, but also prepares us for future employment landscapes that may be dominated by AI and automation.
Impact of AI on Labor Market and Job Roles
The impact of AI on the labor market cannot be overstated, as it signifies both opportunity and disruption across various sectors. David Deming’s study indicates that AI could induce changes reminiscent of the general-purpose technologies that previously reshaped the economy. For working professionals, this shifting landscape calls for adaptability. Roles within sectors like finance, management, and journalism are increasingly exposed to automation risks, compelling knowledge workers to upskill or pivot their careers to remain relevant.
Moreover, AI’s integration has led to a noticeable structural shift, marking an end to the fears of job polarization. Rather than yielding a job market filled with low-wage positions, the study indicates a rise in well-compensated roles that demand advanced training and skills. Interestingly, this shift coincides with a robust increase in STEM job opportunities, hinting that while some jobs may vanish, others are rapidly evolving to align with technological advancements. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for workers as this evolution of AI continues to shape the future of work.
Automation Anxiety: Historical Context and Future Perspectives
Since the 2013 report suggesting that nearly half of U.S. jobs were vulnerable to automation, concerns have proliferated regarding the implications of AI-induced job displacement. However, Deming’s findings highlight that the rate of job disruption has decelerated since 1990, revealing not a crisis but a nuanced landscape of job stability. While many feared an immediate wave of job loss, the actual data provides a more encouraging perspective, demonstrating that automation has not wreaked havoc on employment numbers as anticipated.
Nevertheless, anxiety over automation persists, reflecting a broader societal concern regarding technology and employment. As industries evolve, a certain level of occupational churn is inevitable, and Deming suggests that the pandemic has merely expedited trends that were already in motion. Companies seeking to boost productivity amidst economic constraints are beginning to prioritize technology, urging workers to reassess their roles and prepare for the future workforce. The era of automation anxiety may soon transform into an opportunity for growth, provided that workers and companies alike remain proactive in navigating this transition.
STEM Job Growth and Opportunities in the Tech Era
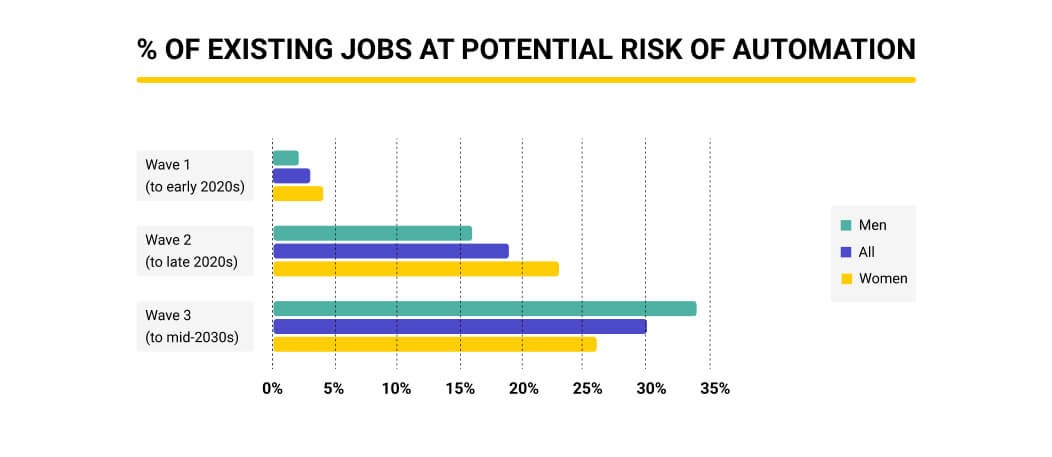
The surge in STEM job growth has been one of the most positive outcomes of technological advancement in the labor market. With a remarkable increase from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% projected by 2024, it’s evident that industries are investing heavily in tech talent. This growth represents not only an increasing demand for skilled workers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics but also a shift towards a more innovation-driven economy. Organizations are increasingly recognizing that to remain competitive, they must harness the capabilities of AI and other emerging technologies, thereby fueling more opportunities in high-skill job sectors.
Furthermore, the focus on STEM education is vital for preparing the workforce of the future. As traditional roles decline, educational institutions and businesses need to collaborate, ensuring that the curriculum is aligned with market needs. Promoting STEM fields is essential not only to fill existing positions but also to inspire the next generation to pursue careers in these critical areas. By prioritizing the growth of STEM jobs, society can harness the potential of technology while also addressing the challenges posed by occupational churn and job displacement.
Job Polarization and Its Decline in the AI Era
Traditionally, job polarization has characterized the labor market, where low-wage jobs flourished at the bottom while middle-skill positions dwindled. However, Deming’s research suggests a significant shift attributed to advancements in AI and technology. The end of job polarization, as reported in the study, indicates a reinvigoration of middle-skill jobs that pay well and require higher qualifications, offering a silver lining to those worried about the future of work. This emerging trend signifies a wake-up call for workers to seek training and education in areas where demand is expanding.
The newfound attention on high-skilled jobs contrasts sharply with concerns surrounding low-paid service employment as these positions face notable declines. The rise of artificial intelligence and automation has prompted industries to reevaluate their workforce strategies, leading to a preference for highly skilled professionals. As this trajectory continues, upskilling becomes essential not only for workers in at-risk jobs but also for those navigating this transformed labor landscape.
The Role of Consumer Behavior in Shaping Job Opportunities
Consumer behavior has undergone dramatic transformations, especially in the wake of the pandemic, influencing labor market dynamics significantly. The shift toward e-commerce, propelled by the necessity to adapt during lockdowns, has reshaped retail sectors markedly. As traditional retail roles decline, industries pivot to technologies like predictive AI that enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. This evolution reflects a broader trend where technology directly aligns with changing consumer preferences, creating new job opportunities in tech-driven service sectors.
As companies invest more in e-commerce and digital solutions, the demand for workers skilled in technology is surging. Job seekers must be agile, learning skills that resonate with these new industry needs. This delicate interplay between consumer behavior and job availability is pivotal; understanding current trends allows both employers and employees to anticipate market demands. A proactive stance toward adapting to consumer-driven sectors can spawn a wealth of job opportunities in emerging markets, creating a parallel path to traditional employment.
Navigating the Challenges of Job Automation in Knowledge Sectors
As organizations increasingly integrate AI into operations, knowledge workers in various industries face unique challenges regarding job security and role evolution. Fields like finance, journalism, and management are particularly vulnerable as AI technologies enhance efficiency, often at the expense of human labor. Workers in these sectors must cultivate versatility, refining their skills to complement technological advancements without falling prey to obsolescence. The historical context provides insight into how such transitions have unfolded and reinforces the importance of adaptability in the face of evolving job landscapes.
Moreover, companies are expected to raise the bar for knowledge workers, pushing for higher outputs amidst economic challenges. The fusion of AI with human labor signifies not a replacement but a partnership, calling for a reimagining of work roles. As employees embrace this transformation, they should pursue continuous learning and anticipate the implications of AI on their professional trajectories. Engaging with emerging technologies and fostering a mindset of adaptability will be essential for securing a foothold in the future of work.
Future of Work: Adapting to Changing Job Landscapes
As we gaze into the future, the work environment appears poised for a fundamental shift driven by technological innovation. The findings of Deming’s research illustrate the necessity for a proactive approach to shaping the future of work. With AI’s influence broadening, professionals across various sectors need to anticipate and adapt to the evolving demands of the labor market. In this landscape, careers will not only be shaped by industry trends but also by the skills individuals choose to cultivate in tandem with emerging technologies.
Creating a robust framework for future employment requires a combination of continuous education, strategic planning, and adaptive methodologies. By embracing change and being willing to learn, both workers and employers can navigate this transformative era successfully. Engaging actively with the trends surrounding automation, STEM advancements, and evolving job roles will help ensure that both individuals and organizations can thrive amidst the challenges presented by the modern labor market.
The Interplay of Education and Employment in an AI World
Education plays a critical role in shaping career trajectories, especially in a climate influenced by AI and automation. As the demand for STEM jobs increases, educational institutions must evolve to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge to thrive. Child education frameworks must shift to prioritize analytical thinking and technological proficiency, allowing future workers to seamlessly integrate into jobs that leverage AI and complex problem-solving abilities. Investing in education that fosters adaptability encourages a workforce that is prepared for the demands of the future labor market.
Conversely, collaboration between education institutions and industries is essential to align curricula with real-world job requirements. By fostering partnerships, schools and businesses can create internship programs, training sessions, and workshops, thereby facilitating a transition into the workforce that caters to the demands of emerging technologies. In this way, the labor market will benefit from a steady influx of well-equipped, skilled professionals ready to navigate and innovate within a rapidly changing environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of AI on the labor market today?
The impact of AI on the labor market today is significant, characterized by shifts in job opportunities, particularly in high-skill sectors. Research indicates that while there was stability in occupational churn from 1990 to 2017, a noticeable change has emerged since 2019, marking a potential trend akin to historic technological revolutions. AI is not just concerned with job displacement; it is also driving the demand for skills in STEM fields, which have expanded to nearly 10% of the labor market by 2024.
How does AI job disruption affect middle-class employment?
AI job disruption affects middle-class employment by changing the landscape of available jobs. Contrary to fears of widespread job loss, recent studies suggest an end to job polarization, with more high-skilled positions emerging. However, this shift may still lead to the decline of certain middle-class roles traditionally supported by low-paid service jobs, signaling a transformation in how labor is valued and structured in a technology-driven economy.
What trends are emerging in the future of work due to AI advancements?
The future of work is seeing several trends due to AI advancements, including a dramatic rise in STEM jobs as companies invest heavily in technology. Additionally, there is a decline in low-paid service roles and jobs in retail, as online shopping and automation become more prevalent. Another trend is the increasing expectation for knowledge workers to adapt quickly to technological changes, with AI enhancing productivity and reshaping work dynamics.
How is occupational churn influenced by AI and technology?
Occupational churn has been influenced by AI and technology by creating both volatility and stability in the labor market. Historical research shows notable disruptions during past technological shifts. Since 2019, there has been renewed dynamism, with a shift in job structures—emphasizing the transitioning workforce from low-paid jobs to higher-skilled roles driven by AI, ultimately affecting how occupations share in the labor market.
What role do STEM job growth and AI play in shaping employment opportunities?
STEM job growth plays a crucial role in shaping employment opportunities, largely driven by AI developments. As companies adopt emerging technologies, the demand for tech-savvy professionals has increased significantly, reflecting a commitment to innovation. This trend presents new opportunities for workers willing to acquire necessary skills in technology and data analysis, as AI continues to reshape various sectors of the economy.
What are the implications of technology and employment on job security?
The implications of technology and employment on job security are profound, particularly due to the growing presence of AI. While technology can create new job opportunities, it also raises concerns about job displacement, especially in knowledge-based occupations. Workers in sectors such as finance, management, and journalism need to adapt to rapidly changing environments to maintain job security, as AI tools streamline functions and increase productivity demands.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Occupational Churn | A term to describe changes in job roles and their market share over time, significant for measuring technological impact. |
| Stable Labor Market Period (1990-2017) | Contrary to fears about tech replacing jobs, this period showed low occupational churn. |
| Emerging Trends Post-2019 | Data revealed notable shifts signaling changes in the labor market dynamics. |
| Job Polarization | With AI, there’s been a reversal with well-paying jobs growing, counter to earlier trends of job polarization. |
| Increase in STEM Jobs | STEM job growth surged from 6.5% to nearly 10% from 2010 to 2024. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Jobs | Employment in low-paid service jobs is declining, marking a potential long-term trend. |
| Retail Job Reduction | Retail jobs decreased by 25% from 2013 to 2023, influenced by e-commerce and AI. |
Summary
The impact of AI on the labor market is profound, as highlighted by recent findings that reveal a landscape undergoing significant transformation. While traditional views suggested a stable job environment for nearly three decades, emerging data post-2019 indicates rapid shifts likely influenced by AI technology. The labor market is experiencing not only a reduction in job polarization, with more high-skilled positions available, but also a dramatic rise in STEM jobs and a decline in lower-paid service roles. This dual trajectory illustrates the necessity for the workforce to adapt and respond to technological advancements, emphasizing the importance of continual skill development and awareness of AI’s ramifications on employment opportunities.